- Solvents are components present in larger amounts
- Solutes are componets present in smaller amounts
- A solute is soluble in a solvent if it dissolves to form a homogenous mixture
- A saturated solution contains as much solute as possible
- An unsaturated solution can dissolve more solute
- Solubility is the measure of how much solute can dissolve in a given solution (g/L, g/ml, mol/L, ppm)
- The solubility of Ba (NO3)2in water is 63 g/100 mL @ 25 degrees Celcius while the solubilty of Ba(NO3)2 in alcohol is is 1.6 g/ 100 mL @ 25 degrees Celcius
Solubility is affected by:
1. heat
2. changing the solvent
3. changing the solute
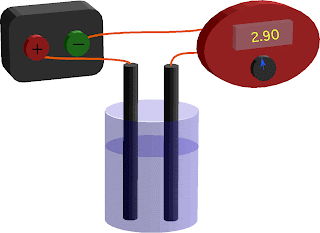
- Measuring the conductivity of a solution
APRIL 14 CLASS NOTES
- Distilled water is non-conductive
- By adding salts, we increase the conductivity
- Electrical conduction in solutions requires charged ions to be present.
- Ionic solutions dissociate (break apart) when placed in water. Molecular solutions do not usually split into ions
Ex: Dissociation of sodium chloride:
NaCl --> Na + Cl
Steps to determine conductivity:
Follow these steps to determine if the solution is conductive:
Ask...
Is it a metal?
Yes = conductive. No ask...
Is it a solid non-metal?
Yes = non-conductive. No ask...
Is it an acid or base?
Yes = conductive. If noask...
Is it ionic?
Yes = conductive. no = non-conductive.
No comments:
Post a Comment